
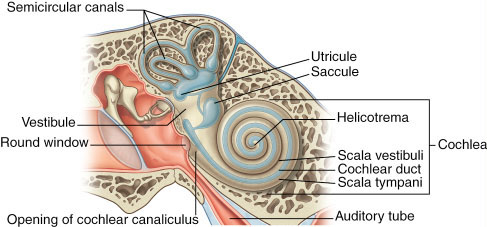
Wanna, G.B., Noble, J.H., Carlson, M.L., Gifford, R.H., Dietrich, M.S., Haynes, D.S., Dawant, B.M., & Labadie, R.F.(2015) Impact of intrascalar electrode location, electrode type, and angular insertion depth on residual hearing in cochlear implant patients: Preliminary results. Wanna, G.B., Noble, J.H., Gifford, R.H., Dietrich, M.S., Sweeney, A.D., Zhang, D., Dawant, B.M., Rivas, A., & Labadie, R.F.(2008) The endocochlear potential depends on two K+ diffusion potentials and an electrical barrier in the stria vascularis of the inner ear. Nin, F., Hibino, H., Doi, K., Suzuki, T., Hisa, Y., & Kurachi, Y.(2013) Factors affecting open-set word recognition in adults with cochlear implants. Holden, L.K, Finley, C.C., Firszt, J.B., Holden, T.A., Brenner, C, Potts, L.G., Gotter, B.D., Vanderhoof, S.S., Mispagel, K., Heydebrand, G., & Skinner, M.W.Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology, 1: 169–174. The importance of electrode location in cochlear implantation. Please contact your local MED-EL representative for more information. * Not all products and features shown are available in all areas. Not all products, features, or indications shown are approved in all countries. Subscribe today to make sure you don’t miss part two of this post! In part two, we’ll take a look at how surgical approach and electrode array design can significantly impact the likelihood of structure preservation during cochlear implantation. But is it possible to effectively reduce the risk of electrode deviation? So it’s fair to say that electrode deviation should be avoided whenever possible. Intact natural hearing structures for future therapies 3Ĭlearly, the ideal outcome for any cochlear implant patient would be an array fully within the scala tympani.Preservation the neural reserve of the patient 1,3.Possibility of residual natural hearing function 3,4.Significantly better speech perception scores 2,5,6.There are the tangible benefits of better speech perception and possibility of useful residual hearing-but there’s also the preservation of neural structures and the natural hearing pathway for future therapies. In contrast, an electrode array placed fully within the scala tympani offers many benefits. Significantly lower speech perception scores 2,5,6.An electrode in scala vestibuli is more likely to stimulate spiral ganglion cells in more than one turn, leading to cross-turn stimulation and pitch confusion. Preserving cochlear structures isn’t only important for candidates with residual hearing. If these fluids are able to mix, the ion gradient and the endocochlear potential would both be lost. So if an electrode array deviates from the scala tympani into the scala vestibuli, it would damage the basilar membrane and the endolymph and perilymph could mix. The endolymph is contained in the scala media, between the basilar membrane and Reissner’s membrane. Perilymph (scala tympani & scala vestibuli) has low K+ and high Na+ (~0 mV).Endolymph (scala media) has high K+ and low Na+ (+80 mV).This potential is essential for any natural inner ear function-without this ion gradient, hair cells would likely not be able to initiate action potentials in the auditory nerve. Between the endolymph and the perilymph, there’s a battery-like electrochemical ion gradient that’s necessary for maintaining the endocochlear potential. Let’s start by taking a look at the intracochlear fluids. However, the basilar membrane and other cochlear structures are extremely fragile-so it’s no surprise that, depending on design and other factors, electrode arrays may deviate from the scala tympani into the scala vestibuli. 2 This enables accurate tonotopic mapping as described by the Greenwood function. 1 In the scala tympani, the array rests below the basilar membrane and stimulates neural tissues in the immediate turn, including spiral ganglion cells, neurites, and axons. The scala tympani is the optimal location for a cochlear implant array.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
